Understanding Menopause – A Natural Transition in a Woman’s Life
Menopause marks one of the most significant biological transitions in a woman’s life. It is the natural cessation of menstrual cycles, officially diagnosed after twelve consecutive months without a period. For most women, menopause occurs between
the ages of 45 and 55, though it can begin earlier or later due to genetics, health conditions, or medical interventions.This phase, while often accompanied by physical and emotional challenges, is not a disease or disorder. Rather, it is a profound transformation—a shift that signals the end of reproductive capability and the beginning of a new stage in life.
The Stages of Menopause
Menopause is not a single event, but a process that unfolds in stages:
Perimenopause: This transitional phase can begin several years before menopause, often in a woman’s 40s. During perimenopause, the ovaries gradually produce less estrogen, leading to irregular periods and the onset of symptoms like hot flashes, night sweats, mood changes, and sleep disturbances.
Menopause: This is officially reached when a woman has gone twelve months without menstruating. At this point, the ovaries have significantly reduced estrogen and progesterone production.
Postmenopause: The years following menopause. Although many symptoms subside, changes in hormone levels continue to influence health and wellness, including bone density, cardiovascular function, and metabolism.
Common Symptoms and Their Impact
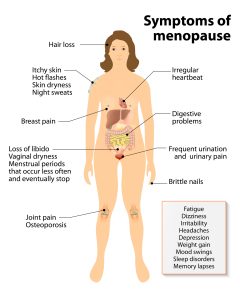
Each woman’s experience of menopause is unique. Some may pass through it with little discomfort, while others face significant physical and emotional hurdles. Common symptoms include:
Hot Flashes and Night Sweats: Sudden feelings of warmth that may cause sweating and flushed skin.
Mood Swings and Anxiety: Hormonal fluctuations can influence neurotransmitters, affecting emotional regulation.
Sleep Disturbances: Insomnia or disrupted sleep patterns can lead to fatigue and irritability.
Vaginal Dryness and Libido Changes: Decreased estrogen affects the elasticity and lubrication of vaginal tissues.
Cognitive Changes: Difficulty with concentration and memory—sometimes referred to as “brain fog.”
Embracing the Change
Menopause is not simply an ending—it is also a beginning. Many women describe a sense of empowerment and freedom in the postmenopausal years, freed from the demands of monthly cycles or the concerns of contraception. It can be a time of rediscovery, of deepening self-awareness, and of focusing on personal well-being.
Lifestyle adjustments can significantly ease the transition. A balanced diet, regular exercise, mindfulness practices, and strong social support can help mitigate symptoms and improve overall quality of life. Additionally, therapies such as hormone replacement therapy (HRT), natural supplements, and integrative approaches like acupuncture or bioacoustic feedback are options to explore based on individual needs and preferences.
The Thyroid in Menopausal Women
If you are experiencing Menopause you will probably know the discomfort of heat flashes or night sweats. The link between thyroid and menopause is significant as both conditions share similar symptoms and can influence each other. Hypothyroidism, or underactivethyroid, is more common in women, especially during menopausal age. The decrease in estrogen levels during menopause can affect thyroid 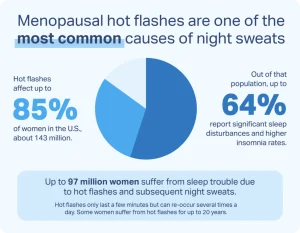 function, leading to overlapping symptoms such as fatigue, mood swings, and weight changes. It is crucial for women experiencing menopausal symptoms to consider the possibility of thyroid issues and consult with their healthcare provider for proper evaluation and management.
function, leading to overlapping symptoms such as fatigue, mood swings, and weight changes. It is crucial for women experiencing menopausal symptoms to consider the possibility of thyroid issues and consult with their healthcare provider for proper evaluation and management.
Understanding the relationship between thyroid health and menopause is essential for managing symptoms and potential
complications associated with both conditions. Thyroid function can influence the severity of menopausal symptoms, as hormonal changes during menopause may affect thyroid hormone production.
What are night sweats and what causes them?
Night sweats are episodes of intense sweating that can soak through your clothes and bedding, disturbing your sleep. They are not the same as the normal sweating that helps regulate your body temperature. Instead, they are a response to a trigger, such as hormonal changes or an underlying medical condition.
There are several causes of night sweats, including:
- Hormonal changes: Fluctuations in hormone levels during menopause, perimenopause, pregnancy, or as a result of conditions like primary ovarian insufficiency (POI) can cause night sweats. These hormonal changes can affect the part of the brain that controls body heat (the hypothalamus), leading to a glitch in the body’s internal thermostat and causing night sweats as a cooling mechanism.
- Medications: Certain medications can cause night sweats as a side effect. These include some antidepressants, hormonal therapies, and steroids.
- Underlying medical conditions: Night sweats can be a sign of various underlying medical conditions, including infections (such as tuberculosis or endocarditis), cancer (such as lymphoma), neurological disorders (such as autonomic dysreflexia), and endocrine disorders (such as hyperthyroidism). It is essential to consult a healthcare provider if you experience night sweats alongside other symptoms to rule out any underlying medical conditions.
- Hyperhidrosis: This is a condition characterized by excessive sweating not related to any apparent reason or underlying medical condition.
Natural Approaches
Estrogen/Progesterone Support:
Foods rich in phytoestrogens (e.g., flaxseed, soy)
Black cohosh, red clover, maca root (under guidance)
Thyroid Regulation:
Iodine-rich foods (seaweed, eggs), selenium (Brazil nuts)
Reduce processed sugar and gluten if sensitive
Adrenal Support:
Adaptogens (ashwagandha, rhodiola, holy basil)
Stress reduction, yoga, mindfulness
Blood Sugar Balance:
Balanced meals with protein, fiber, healthy fats
Avoid high-sugar snacks before bed
Medical Options
Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT):
Estrogen, progesterone, or combination therapy
Bioidentical hormones as an alternative
Thyroid Medications:
Levothyroxine or other treatments for hyper/hypothyroidism
Testosterone Therapy (for men or women when indicated)
Insulin Management:
Medication or dietary regulation for diabetes or prediabetes
Sleep Aids (if sleep is severely affected):
Prescribed under medical guidance
How Bioacoustic Therapy Can Help with Night Sweats
What Is Bioacoustic Therapy?
Bioacoustic therapy involves using the body’s own voice frequencies or sound-based interventions (like tones and vibrations) to assess and influence health. Developed by Sharry Edwards and others in the field of vocal profiling, this method believes that the voice reflects the health status of the body—particularly biochemical and hormonal states.
1. Regulating the Autonomic Nervous System
Night sweats are often triggered by overactivation of the sympathetic nervous system, especially under stress. Bioacoustic therapy uses specific frequencies to:
Promote parasympathetic (rest-and-digest) activity
Reduce cortisol spikes at night
Calm the nervous system and promote restful sleep
️ 2. Stabilizing Thermoregulation Centers
Certain brain regions like the hypothalamus control body temperature. Hormonal changes (especially estrogen drops) affect its stability.
Bioacoustic frequencies can:
Help retrain or balance hypothalamic function
Reduce temperature sensitivity and minimize hot flashes or night sweats
⚖️ 3. Balancing Hormonal Output
Bioacoustics practitioners often analyze vocal frequencies to identify imbalances in:
Estrogen, progesterone, testosterone
Thyroid hormones
Cortisol and adrenaline
Once imbalances are detected, targeted sound frequencies can be used to:
Encourage more optimal hormone expression
Support glandular activity (e.g., thyroid, adrenals, ovaries)
4. Improving Sleep Cycles
By calming the brain and rebalancing neurotransmitters (like serotonin and melatonin), bioacoustic tones can help:
Reduce wakefulness caused by night sweats
⚠️ Important Notes
Bioacoustic therapy is non-invasive and often complements other treatments.
It’s not a substitute for medical diagnosis or hormone therapy, but a powerful adjunctive modality.
Sessions typically include a voiceprint analysis and a customized set of tones to be listened to over days or weeks.
BioAcoustic Menopause Research : We have successfully been able to assess the root cause of the night sweats or hormonal imbalances and to re-balance these hormone levels and the thyroid functioning with sound presentation, to completely remove night sweats and other hormonal symptoms associated with Menopause.



